
Therefore, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius.

Atomic radius of element free#
However, this assumes the atom to exhibit a spherical shape, which is only obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus. It must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. The atomic radius of Californium atom is –pm (covalent radius). Note that, each element may contain more isotopes, therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occuring isotopes and their abundance. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. Step 2: Determine the positions of elements in the periodic table to predict. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Californium are 248-254. We know that atomic radius decreases along the period and increases down the group. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Atomic radius, non-bonded Half of the distance between two unbonded atoms of the same element when the electrostatic forces are balanced. 9-57: Å Å Element Symbol R v d W ( Å) R c o v ( Å) Chlorine C l 1.75 1. From the recent edition of CRC Handbook 1, p.
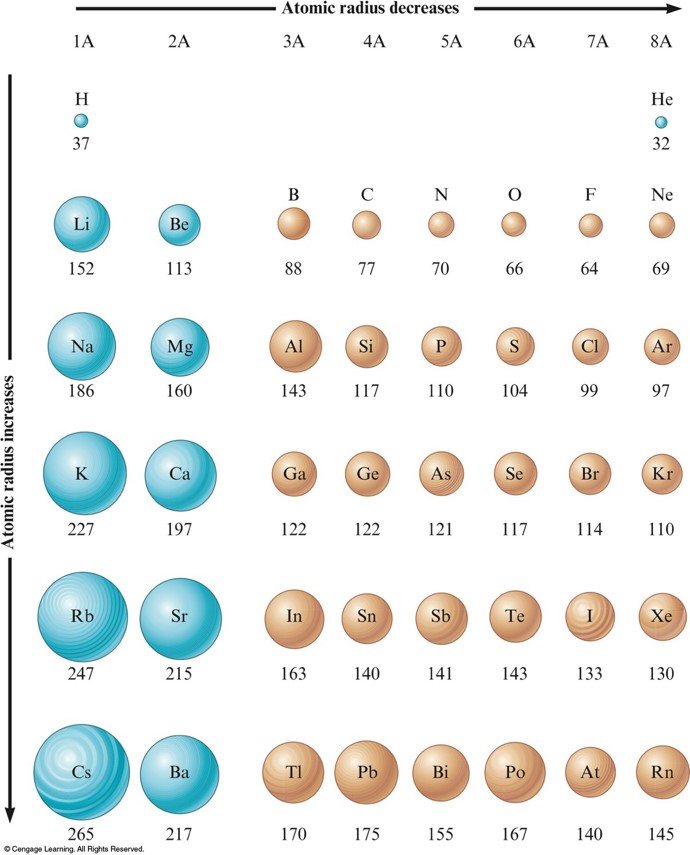
The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.įor stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. An atomic radius is a class consisting of van der Waals radii R v d W (steric interactions), covalent radii R c o v, and ionic radii R i (and some other as well). Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. These trends explain the periodicity observed in the elemental properties of atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity.Atomic Number – Protons, Electrons and Neutrons in CaliforniumĬalifornium is a chemical element with atomic number 98 which means there are 98 protons in its nucleus. This happens because the number of filled principal energy levels (which shield the outermost electrons from attraction to the nucleus) increases downward within each group. Second, moving down a column in the periodic table, the outermost electrons become less tightly bound to the nucleus. As this happens, the electrons of the outermost shell experience increasingly strong nuclear attraction, so the electrons become closer to the nucleus and more tightly bound to it. First, electrons are added one at a time moving from left to right across a period. In addition to this activity, there are two other important trends. Stable octets are seen in the inert gases, or noble gases, of Group VIII of the periodic table. Elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve stable octet formation. In a group, on moving from top to bottom, the ionic radius increases as a new energy level is added at each succeeding element but the number of valence. These trends can be predicted merely by examing the periodic table and can be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements.

The periodic table arranges the elements by periodic properties, which are recurring trends in physical and chemical characteristics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
